
EPDM Basics: Chemical Compatibility and Important Benefits You Need to Know
June 27, 2022 · Tinu George
Before getting to know about EPDM Rubber, let's have a look upon Rubber. When the word rubber comes to mind we probably think of tyres, rubber bands, gloves, erasers etc. But the actual range of applications and products can blow up our minds. It is been widely used in the manufacturing of thousands of products and the areas of application spans around the whole world from home/ kitchen utensils to defense, construction to outer space, toys to automotive, agriculture to shipping etc. Where ever you go, you will be able to see and feel it, but in different forms.
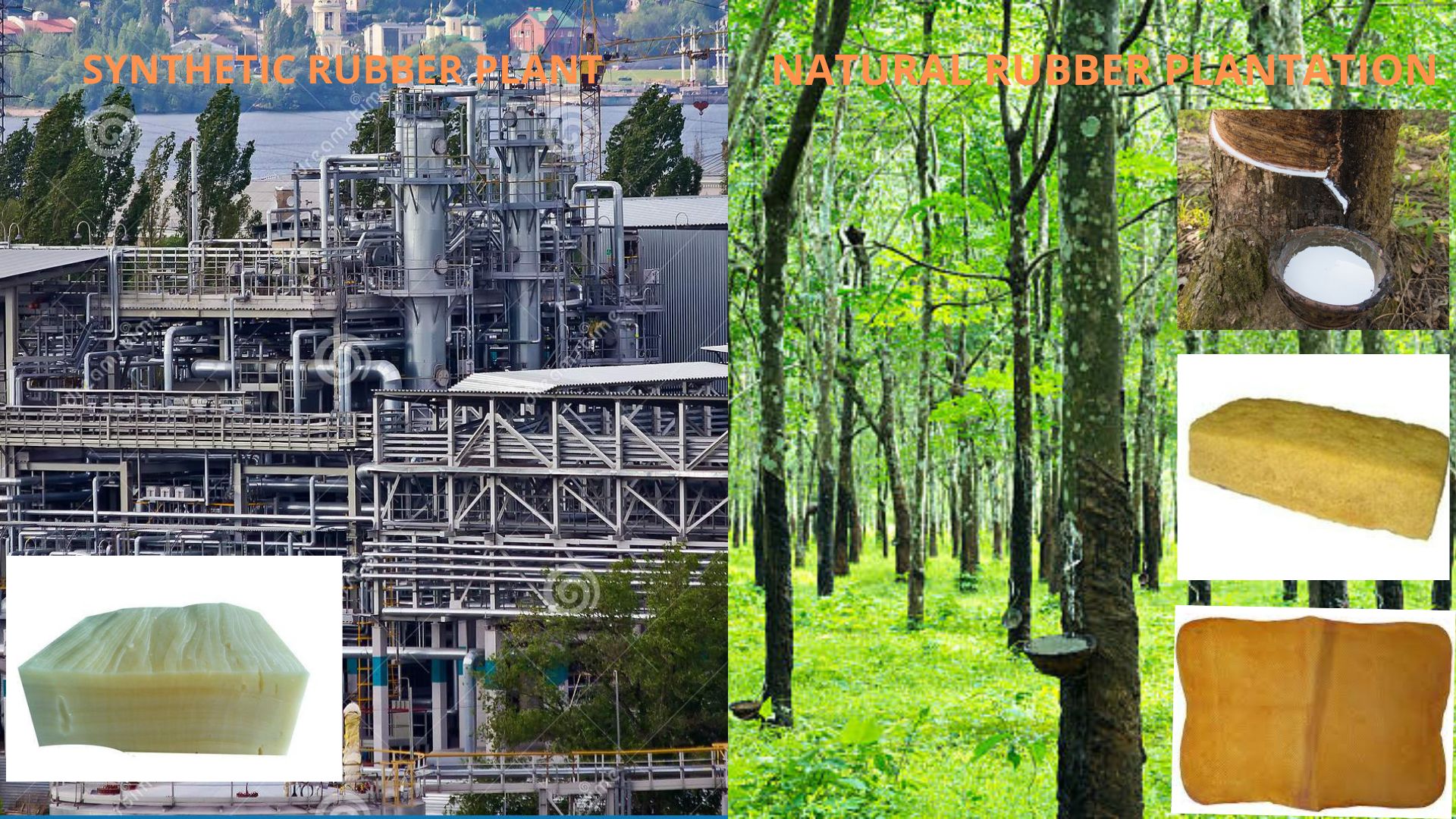
We can classify Rubber into two types

-
Natural Rubber
-
Synthetic Rubber.
As the name indicates, the Natural Rubber is made from the white milky liquid called Latex that comes from a tree species called Hevea brasiliens, often known as Rubber tree.
And synthetic rubbers are made in chemical plants by synthesizing from petroleum byproducts and other minerals. It is basically an artificial polymer which has the property of undergoing elastic stretch ability or deformation under stress and can return to its previous form without permanent deformation.
Any Rubber in its raw form cannot be used for the manufacturing process. In the raw form, the molecules in rubber are long chains that are tangled up and that links will be weaker. Here comes the process called the Vulcanization. We add certain chemicals such as Sulphur which acts as the main crosslinking agent and others such as Activators, Accelerators, Pre-vulcanizing inhabitants, Anti-oxidant agents etc. to the rubber to achieve the required properties. The added sulphur atoms help to form extra bonds between the rubber molecules, which are known as cross-links. The weaker links will become stronger cross-links, tying the molecules together, thus making them harder to pull apart. Depending on the chemicals added the properties can be varied and can be very hard, soft, resilient etc. Check out rubber chemical dispersion manufacturer in Kerala
Why Synthetic Rubber?
Over the years we have seen a drastic use of Synthetic Rubber instead of natural rubber in many areas. That is because when we require improved material properties synthetic rubber is mostly preferred. There are approximately 20 different chemical types of synthetic rubber and within all of the types of rubber, there are different grades. Each one has got different properties and advantages. Some of the major Synthetic Rubbers are
- Chloroprene/Neoprene Rubber
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
- Nitrile Rubber
- Silicone Rubber
- Isoprene Rubber
- Hypalon etc
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) Rubber
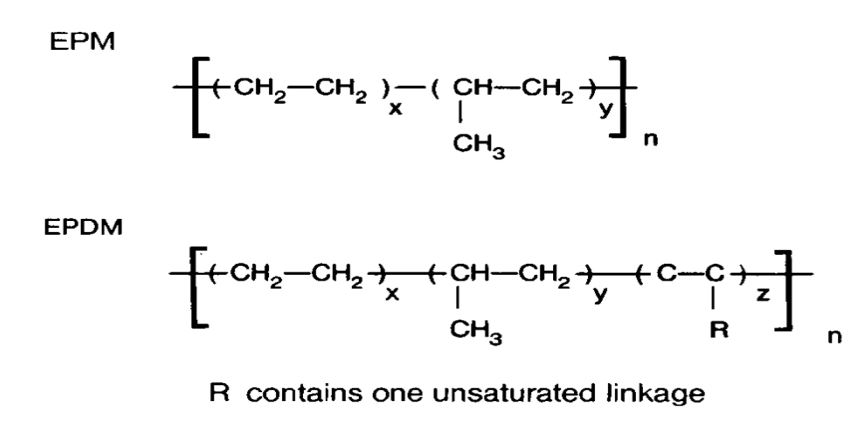
EPDM gets its name from the chemicals (monomers) ethylene, propylene and diene that are mixed together in various proportions to form it. The ethylene content is usually between 45% to 75%. EPDM was introduced in the USA in 1962. Since then it has been used in various industries and for wide range of applications that ranges from automotive products to space projects. Excellent resistance to weather, ageing, ozone, heat and other excellent electrical properties makes EPDM one of the favorites. Check out epdm rubber products
The Properties of EPDM Rubber
• Temperature Range
Low Temperature Range: -29°C to -51°C
High Temperature Range: Up to 177°C
• Tensile Strength
Tensile Range: 500-2500 P.S.I.
Elongation: 600% Maximum
Hardness - Range: 30-90 Shore A
Aging Weather: Excellent
Abrasion Resistance: Good
Tear Resistance: Fair
Solvent Resistance: Poor
Oil Resistance: Poor
Compression Set: Good
The diene monomers of the EPDM provide the cross-linking that gives it its standalone properties like immense resilience, flexibility and durability. Also the higher filler loading ability makes it an industrial friendly synthetic rubber. Eventhough EPDM has got a good tensile strength, it is not usually used in the manufacturing of rigid parts due to its flexibility. But for flexible articles/parts such as Hoses, O rings, washers etc., EPDM are preferred widely due to the above mentioned properties.
Applications
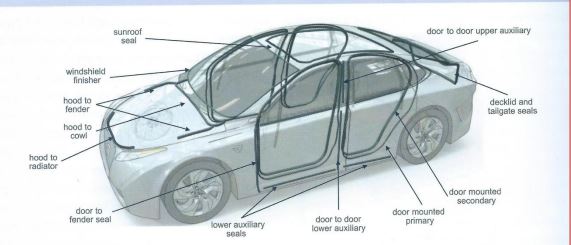
- Automotive – EPDM artilcle comprises many of the components inside an automotive which includes Hoses, Beadings, Grommets, Mud flaps, Hydraulic brake systems, Weather seals, window spacers, Electrical insulations etc.
- Industrial – Tubes, grommets, O-ring, hoses, gaskets etc
- Agriculture – Again it comes partially under automotive – Many EPDM articles are been used in the assembly of tractors and Tillers. Oil/Water sealants, grips, Mud flaps etc
The range of EPDM’s application is limitless and here some of the major applications have been mentioned.
Quick Enquiry
To know more about Associated Chemicals feel free to send a message
 Our Sister Concerns
Our Sister Concerns 


Usefull Links
Get In Touch
Assochem Chambers, Bypass, Edapally,
Kochi-682024, Kerala, India.
Phones : +91 9495999349, +91 9388610189, +91 484 2339190, +91 484 2348028
E-mail : nsn@assochem.in, marketing@assochem.in, mail@assochem.in
Support

















