
SYNTHETIC RUBBERS
March 31, 2025 · Neethu A S
A Synthetic rubber is any artificial elastomer, which is manmade is termed Synthetic rubber. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum by products. Synthetic rubber(elastomers) is long chain polymer with special chemical and physical as well as mechanical properties. These materials have chemical stability high abrasion resistance, strength and good dimensional stability.
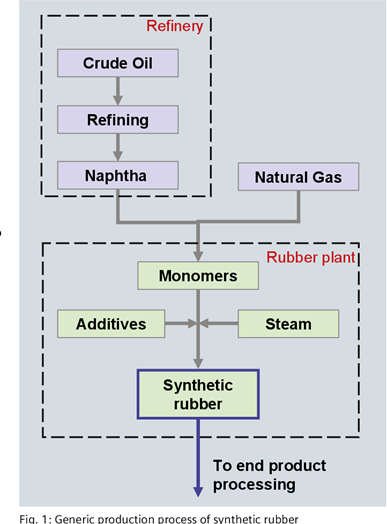
The Synthetic rubber production begins with oil, coal, or other hydrocarbon processing. Naphtha is produced during the refining process. The naphtha is extracted and can then be mixed with natural gas to create monomers such as styrene and isoprene essential for the manufacturing of synthetic rubber.
FORMS OF SYNTHETIC RUBBERS
Synthetic rubber enters commerce in one of three basic forms
- Latex: These are typically used for articles that are coated or dipped
Example: fabric coating rubber gloves.
- Solid: These are usually processed by extrusion or calendaring
Example: Tire and rubber goods manufacture
- Powder: These are generally used in fine coating application.
TYPES OF SYNTHETIC RUBBER
There are types of general-purpose synthetic rubbers produced commercially
1. SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber)
Styrene-butadiene rubber is the largest-volume synthetic rubber produced today. It is produced from the monomers styrene and butadiene and is commercially available in three main forms-- solid, latex, and carboxylate. The relative proportions of styrene and butadiene can vary but are typically 75 percent butadiene to 25 percent styrene. If the styrene content is less than approximately 50 percent, the resulting polymer is rubbery; however, as styrene content increases beyond 50 percent, the polymer becomes harder, more like a plastic, and less elastic in nature.
SBR's main use is in the production of tires, although some may be used in industrial rubber goods such as gaskets and hoses.

2. Butadiene Rubber
Butadiene rubber is the second-largest commercially produced rubber behind SBR. Polymerization of butadiene can result in a number of isomers, but the predominant one in commercial applications is the cis-1,4- structure, which is similar in structure to natural rubber. Butadiene rubber possesses excellent heat and abrasion resistance and good low-temperature properties. It is mainly used in tire and belting applications.

3. EPM/EPDM
Ethylene-propylene monomer (EPM) and ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) rubbers are similar because they are produced primarily from ethylene and propylene petrochemical raw materials. However, EPDM contains a third monomer, a diene, in addition to ethylene and propylene. Most ethylene-propylene rubbers produced are of the EPDM type. Ethylene-propylene rubbers are characterized by their outstanding resistance to heat, light, oxygen, and ozone. End uses for ethylene-propylene rubbers are varied, but include tires, automotive components, sheeting, roofing barriers, and hose and belting applications.

4. Nitrile rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber, also known as acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber, is a synthetic rubber produced by the copolymerization of butadiene and acrylonitrile. Nitrile rubber is characterized primarily by a high degree of resistance to petroleum chemicals and by superior flexibility at low temperatures. Thus, it is principally used in applications such as industrial rubber goods (hoses and belting), seals and gaskets, adhesives, footwear, and wire and cable insulation. Nitrile rubber is used in latex as well as solid forms.

5. Butyl (isobutylene-isoprene) rubber
Butyl rubber is made from the polymerization of isobutylene and a small amount of isoprene to produce polymethylpropene-co-2-methyl-1,3-butadiene. Compared with other rubbers, butyl rubber is distinguished by its high level of impermeability to gases and low thermal expansion. Due to these physical properties, butyl rubber is mainly used in tire applications, especially in the manufacture of inner tubes, tire inner liners, and sidewall construction. Relatively minor end-use applications include rubber mechanical goods, paper coatings, and electrical applications.

6. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene)
Polychloroprene is the name for a family of synthetic rubbers based on the chemical chloroprene. The chloroprene rubbers are noted for their high resilience and excellent resistance to ozone deterioration. Additionally, chloroprene rubbers possess strength and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and aging. As a multipurpose elastomer, chloroprene is used in a wide range of end-use applications. For example, chloroprene rubbers are used in belting, gaskets, hose, wire and cable coverings, and adhesive applications. Chloroprene rubbers are available in both latex and solid forms, but solid forms predominate in the industry.

HOW THE SYNTHETIC RUBBER MADE
There are 5 steps for synthetic rubber processing
Step1: Refine the source material
Step2: Create polymers
Step3: Add chemical agents
Step4: Vulcanisation
Step5: Shaping
Some Benefits of Synthetic rubber
- With stands extreme temperature well.
- Resistant to chemical damage.
- Resistant to damage from sunlight, ozone, and weather.
- Strong electrical insulation.
- Flexible at low temperature
Reference : Google
Quick Enquiry
To know more about Associated Chemicals feel free to send a message
 Our Sister Concerns
Our Sister Concerns 


Usefull Links
Get In Touch
Assochem Chambers, Bypass, Edapally,
Kochi-682024, Kerala, India.
Phones : +91 9495999349, +91 9388610189, +91 484 2339190, +91 484 2348028
E-mail : nsn@assochem.in, marketing@assochem.in, mail@assochem.in
Support

















