
Specifications, Test Procedures And Significance Of 60% Natural Rubber Latex (CL-60)
May 16, 2023 · Preethy Paul

The 2 important international specifications are the
- ISO – Internal Organization for standardization
- ASTM – American Society for Testing and Materials
- Under ISO it is documented in
- ISO 2004:2017 - Natural rubber latex concentrate — Centrifuged or creamed, ammonia-preserved types — Specifications
- And under ASTM it is documented in
- ASTM D-1076 – Standard Specification for Rubber – Concentrated, Ammonia Stabilised, Creamed and Centrifuged natural Latex
SPECIFICATION OF CL-60 AS PER ISO AND ASTM
| Parameter | Unit | Range | ISO | ASTM | |
| 1 | Total Solids (tsc) | % | min* | 61 | 61.3 |
| 2 | Dry Rubber (drc) | % | min | 60 | 59.8 |
| 3 | Non Rubbers (nrs) | % | max | 1.7 | 2 |
| 4 | Alkalinity as Ammonia – HA | % | min | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Alkalinity as Ammonia - LA | % | max | 0.29 | 0.29 | |
| 5 | Mechanical Stability Time (MST)# | sec | min | 650 | 650 |
| 6 | Coagulum Content | % | max | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| 7 | Copper | ppm | max | 8 | 8 |
| 8 | Manganese | ppm | max | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | Sludge Content | % | max | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 10 | Volatile fatty Acid No (VFA) | No | max* | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 11 | KOH No | No | max* | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 12 | pH | Unit | Min | 10 | 10 |
# MST is tested 20 days after production Analysing the Tests separately
- drc being a measure of the rubber content it is important from the commercial point of view. The customer has to get the agreed quantity (60%) of rubber
- tsc is important only because if it is high the nrs (tsc – drc) will be high
- For thin products, especially condoms better film formation is there only if the non rubbers are low.
EPDM rubber products manufacturer in Kerala
TEST METHOD FOR TSC
- For TSC a known weight of latex is weighed into a SS dish or petri dish. This is dried in an air oven
- At 70+2oC for 16 hours or
- At 100+2oC for 2 hours
- The sample is cooled in a desiccator and weighed.
- The sample is further dried and reweighed till the difference is less than 1 mg
- Duplicate samples have to be done and the difference between the 2 samples should not be more than 0.15%
- The average is taken for calculation
- Total solids, % = [(C-A)/(B-A)] x 100
- A= weight of empty vessel
- B= weight of vessel + latex
- C= weight of vessel + dry sample
TEST METHOD FOR DRC
- Weigh 10g of latex into a shallow beaker or evaporating dish and dilute to approx. 25% TSC
- Add 2% ascetic acid very slowly with constant stirring
- Place the vessel on a steam bath for 20 to 30 min A clear serum should be got
- Gather the coagulum into 1 block and pass through lab rollers washing with plenty of water.
- Optimum thickness is 2 mm
- Dry in an air oven at 70+2oC till no white specs are seen
- Cool and weigh the dried sample
- DRC = mass of dried sample/mass of latex x 100
- NRS = TSC - RDC
TEST METHOD FOR ALKALINITY AS AMMONIA
Here we are testing the total alkali present and expressing it as Ammonia
The reagents required are
- 0.1N HCl
- Methyl Red indicator
2 to 5 g of latex is weighed accurately into a conical flask containing 200 ml of distilled water 5 drops of Methyl red indicator is added and swirled well .This is titrated against 0.1N Hcl, the end point is when the colour changes from red to pink
The vol. of HCl used is noted
Normally the calculation is done by substituting in a formula
% of Alkalinity as Ammonia is calculated as
The basic starting point is
NHCl x VHCl = NCL60 x WCL60
If we rewrite this equation: (the unknown is Normality of CL60)
NCL60 = (NHCl x VHCl)/WCL60 hence
Wt of Ammonia = NCL60 x 17/1000
Wt of Ammonia = NCL60 x 17/1000
= [(NHCl x VHCl)/WCL60] x 0.017
% of Ammonia = 0.017x(NHClxVHCl)x100
WCL60
Eq: wt: of Ammonia - 17
MECHANICAL STABILITY TIME
Significance:
This test gives an indication at to how stable the latex is to agitation, the colloidal stability. The stability is crucial in the transport and stirring of CL60
Materials required
• Stirrer – 14000+200 rpm [MST apparatus earlier the KLAXON MST TESTER]
• Test beaker usually polycarbonate
• Glass rod
• Petri dish with water
Conditioning of Latex
- The latex is dilutes to 55 + 0.2% tsc
- Latex warmed to 36 to 37 deg C
- Strain thro 180 micron mesh
- Check if temp 35 + 1 deg C
- Place on the MST holder and start stirring
- The bottom of the stirrer should be 12.70+2.5 mm from the bottom inside of the beaker
Test Procedure
- Start stirring, simultaneously start a stop watch
End point
- The is determined by frequently dipping the latex and pouring a drop in the water in the petri dish or gently rubbing over the palm till the first sign of coagulum is seen
Expression of result
- In seconds from the time of start of stirring to the first appearance of coagulum
DETERMINATION OF COAGULUM CONTENT Significance:
This estimates the coagulated rubber particles the skin formed and other foreign matter in latex. Coagulum can destabilise the latex as well as result in poor film formation
Materials requires
- SS sieve 180 µm sieve with holder (approx. 80 US mesh size)
Test Procedure
- 100g latex weighed and dilute using 100g 5% potassium oleate
- Sieve through the 180 µm sieve [Collect the filtrate for doing the Micro coagulum]
- Wash with 5% K Oleate
- Remove the sieve and dry in an air oven at 100+2 deg C for 30 min
Calculation
- Cool and weigh the sample to constant weight
-
Coagulum Content% = Mass of dried coagulum x 100
Mass of latex taken
DETERMINATION OF MICRO COAGULUM CONTENT
This is a continuation of Coagulum determination and has the same significance as coagulum content
- Sieve Used – 44 µm or 325 mesh size
- The filtrate after the coagulum determination is sieved through the 325 mesh sieve
- Washed with 5% K Oleate soap solution
- Sieve is removed and dried in an air oven at 100+2 deg C for 30 min
- Cool and weigh the sample to constant weight
Calculation
Micro Coagulum Content% =Mass of dired micro coagulum x 100
Mass of latex taken originally
COPPER and MANGANESE were insisted by Customers when Iron pipes, brass or gun metal valves etc were used. Today they have all been replaced by Stainless Steel or PVC and Customers do not insist these test results.
Both Copper and Manganese are done spectrophotometrically
COPPER
A known weight of tsc film is ashed at 800 deg C and digested in Nitric Acid/Hydrochloric Acid mixture.
The colour generating compound is the complex of
Cu + ZDEC
Known solutions with Cu is made and the standard graph made
The Unknown ashed solution is complexed with ZDEC and reading taken ant 425 nm
From the graph the value is determined
MANGANESE
The standard calibration graph is first made using known quantities of Manganese
The reagents used are
- Dilute Sulphuric Acid
- Ortho phosphoric acid
- Potassium Hydrogen Sulphate
- Sodium periodate
This develops the permanganate colour
The colour is read spectrophotometrically at 525 nm
The value is read from the graph directly
SLUDGE CONTENT
Apparatus
Laboratory Centrifuge of rpm 2300 – 3000
With 50 ml centrifuge tubes
Chemical Used
Alcohol – Ammonia mixture
Ammonium hydroxide- 28 ml
Ethyl Alcohol 95% 946 ml
Water 2810 ml
Procedure
50 g each of latex is taken into the centrifuge tubes, the top closed and centrifuged for 20 min. The top sludge is removed and the latex above the sludge is carefully taken out using a pipette.
Ammonia Alcohol mixture is poured into the tubes and the process is repeated till the supernatant liquid is clear
The sludge is then transferred quantitatively into a weighed 200 ml beaker
The water is evaporated on a hot plate and dried at 70+2oC and weighed
Calculation
% of Sludge = mass of sludge x 100
mass of latex
VOLATILE FATTY ACID NO. (VFA NO)
Definition
Volatile fatty Acid No is defined as the Number of Grams of Potassium Hydroxide required to neutralize the Volatile fatty Acids in a latex sample containing 100 g of total solids
Significance
VFA indicates the quality state of the latex at that time with particular reference to the microorganisms present that produce fatty acids.
Apparatus
- Markham Still
- Micro burette
- Steam Generator
Reagents
- Ammonium Sulfate 30% m/m
- Barium Hydroxide 0.01N
- Bromothymol Blue Indicator
- Sulphuric Acid 50% m/m
Markham Still
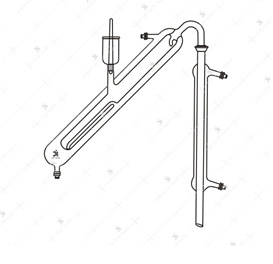
Principle
2CH3COOH + Ba(OH)2 Ba(CH3COO)2 + H2O
Acetic Acid and other similar organic acids react with Barium Hydroxide to give Barium Acetate of similar salts plus water.
Significance
- Weigh 50 g of latex into a beaker and add 50 ml of Am. sulphate (Acid is not used because we are determining the acid present in the latex)
- Place the mixture on a water bath and keep stirring till complete coagulated
- Press out sufficient serum
- Filter the serum and pipette 25 ml serum into a 50 ml conical flask
- Acidify it by adding exactly 5 ml of sulphuric acid, Swirl
The strong acid releases any complexed weak acids
Do not heat at this stage because the volatile acids will be released
The Distillation
- Pass steam through the Markham Still to clean it
- Introduce to the inner tuber 10 ml of the acidified serum
- Place a 250 ml graduated conical flask at the tip of the condenser
- Pass steam into the inner tube, slowly at first.
- Collect 100 ml distillate
- Titrate against 0.01 N Barium Hydroxide using phenolphthalein as indicator. Run a blank with water.
Calculation
67.32 X N x V X 50 + W(100 –drc
W x tsc 100D
Where:
N = Normality of Ba(OH)2
V = Volume of Ba(OH)2
W = weight of sample
D = density of serum (1.02)
KOH Number
Definition
KOH Number is defined as the number of grams of Potassium Hydroxide equivalent all the acid radicles in latex containing 100 g of total solids
Significance
KOH Number is an indication of the age of a well preserved latex.
Apparatus
- pH Meter
- Stirrer
Reagents
- Formaldehyde: 5% solution neutralized with KOH
- Potassium Hydroxide 0.50M (56.106/2 in 1000 ml water): should be carbonate free)
Procedure
- Weigh latex containing 50g of Total Solids
- Adjust the ammonia in latex to 0.50% on water basis by adding 5% formaldehyde
- The required formaldehyde is
= M (100 – TSC) (TA – 0.5)
189
M = Weight of Latex
TA = Total Alkalinity in water phase
1 ml 5% formaldehyde = 0.0189 g of Ammonia
- Dilute the latex to 30% tsc
- Place the latex on a stirrer on measure the pH
- Add 5 ml 0.50M KOH and record the pH after stabilization
- Add 1 ml each KOH at a time and continue measuring the pH
| Vol of KOH | pH | 1st diff | 2nd diff |
| 5 | 9.11 | ||
| 0.13 | |||
| 6 | 9.24 | 0.03 | |
| 0.16 | |||
| 7 | 9.4 | 0.05 | |
| 0.21 | |||
| 8 | 9.61 | 0.07 | |
| 0.28 | |||
| 9 | 9.89 | 0.11 | |
| 0.39 | |||
| 10 | 10.3 | ### | |
| 0.25 | |||
| 11 | 10.5 | ### | |
| 0.19 | |||
| 12 | 10.7 | ### | |
| 0.16 | |||
| 13 | 10.9 |
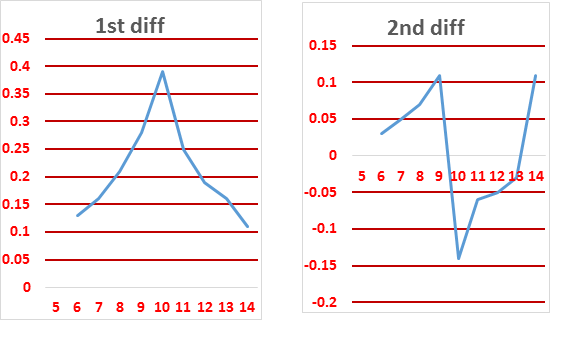
The end point can be found from
1st differential deflection point or
2nd differential intersection point
Calculation
KOH NO: = N x V x 561
W x tsc
Where
N = Normality of KOH
V = Volume of KOH at end point
W = weight of latex sample
pH
Method
pH is determined electronically using a pH meter and glass electrode
Procedure
- Sufficient Latex sample is filtered through 80 mesh sieve to a beaker.
- It is allowed to stand for the bubbles to emerge
- The bubbles are removed
- The latex is warmed to 27+2oC
- The electrode in immersed in the latex and pH directly read
Result
The result is expressed as
pH at 27oC = xx.xx
CHEMICAL STABILITY TESTS
The Chemical Stability tests are
- Brookfield Viscosity (BV)
- Ford Cup Viscosity
- Zinc Oxide Viscosity after 5 min (ZOV5)
- Zinc Oxide Stability after 60 min (ZOV5)
- Zinc Oxide stability (ZST)
- Zinc Oxide Heat stability (ZHST)
These tests are important for manufacturing products like Gloves, Condoms, Catheters, Balloons etc.
Brookfield Viscosity
Brookfield Viscosity denotes the shear viscosity of a liquid. The viscosity of latex is determined at 60 tsc using spindle 2 rotating at 60 rpm at a temperature of 25 + 2oC
Apparatus
- Brookfield viscometer
- 250 ml tall glass beaker
- Thermometer
- 180 micron IS sieve
- The caution when using the viscometer is that the spindle is suspended on a glass pivot hence it should be fitted or removed only by holding the top screw portion
Procedure
- Filter the latex
- Pour about ¾ of the
Container
- Adjust the temp in a ice/water bath to 25oC
- Wait of the air bubbles to emerge and remove it
- Place the test portion on to the viscometer attached with spindle 2
- Level the latex to the mark on the spindle
- Check the spindle _ No 2
- Select the spindle speed to 60 rpm
- Wait for 30 to 45 seconds and note the Brookfield Viscosity reading
Expression of result
The result is expressed as
Brookfield Viscosity sp2, 60 rpm, 60 tsc, 25+2oC, cps
(spindle 2 rotating at 60 rpm and the latex having a tsc of 60%, temperature adjusted to 25+2oC
Units is centipoise (cps)
Zinc Oxide Viscosity (ZOV5 and ZOV60)
Significance and objective
Zinc oxide Dispersion causes destabilization and thickening of latex. Latex with Zinc Oxide dispersion added normally has higher viscosity than one without Zinc Oxide. The Viscosity is measured after 5 minutes and 60 minutes to estimate the thickening.
Procedure
- The latex after measuring the Viscosity is available and can be used for these tests.
- Weigh 320 g of latex and add 5 g of 40% ZnO dispersion (1phr) and stir well. Wait for 5 minutes
- Measure the Brookfield Viscosity
- Keep the sample for 60 minutes (from time of addition of ZnO)
- Measure the Brookfield Viscosity
- Calculation
ZOV5 = BV after 5 min of addition of ZnO x 100
Original BV
- The unit of expression is Percent (%)
- similarly
-
ZOV60 = BV after 60 min of addition of ZnO x 100
Original BV
- The unit of expression is Percent (%)
Zinc Oxide Stability Time (ZST)
Significance
ZST signifies the stability of latex to agitation after the addition of dispersion. A low value if not good
Apparatus
- MST machine
- Test beaker
Procedure
- Take 320 g of latex into the beaker and add 5 g of 40% ZnO dispersion (1 phr)
- Stir well
- Keep for 60 min
- Take 80 g into the MST container
- (Alternatively 80 g of latex can be taken after the ZOV60 test)
- Heat the latex to 35+1oC
- The end point is similar to that for MST
- The value is noted in sec
Zinc Oxide Heat Stability
- ZHST is the stability of the latex to heat after addition of ZnO. If the stability is too high there will be delay in gelling on the hot former and resultant flow down.
- Procedure
- Add 5 g of 40% ZnO dispersion to 320 g of sample and mix well. 50 ml of this sample is taken in a 100 ml beaker, 60 minutes after the addition of ZnO and is heated in a water bath at 90 ± 2OC with constant stirring.
- (Alternatively 50 ml of latex can be taken after the ZOV60 test)
- Continue stirring with periodic removal of the coagulum until complete coagulation takes place.
Result
The result is the time taken from the start of heating to the time of complete coagulation expressed in seconds
FORD CUP VISCOSITY
Significance
Ford Cup viscosity is the flow viscosity of latex and is measured by passing specified quantity of latex through an orifice of specified dimension.
The Apparatus
The apparatus consists of a vessel of capacity 100 ml and an orifice at the bottom. Based on the size of the orifice the FC is numbered
- B1 - 2.10 mm
- B2 - 2.38 mm
- B3 - 3.17 mm
- B4 - 3.97 mm
- B5 - 4.76 mm
- B6 - 7.14 mm
The preparation of sample
The Procedure
The Ford Cup selected (usually B3 for Latex) is placed on the stand and levelled. The bottom is closed with the finger and filtered (80 mesh) latex poured into it. The latex should be free of air bubbles. The edge of a glass plate or rod is run on the top of the cup so that the excess latex flows into the side. The cup outlet is opened by removing the finger; simultaneously starting a stop watch. The stopwatch is stopped at the point when the continuous flow breaks. This is the end point
Expression of Result
- The result is expressed as sec with tsc and temperature
- Ford cup #3 Viscosity
- At 20 tsc and 25+1oC = xx sec
MAGNESIUM
Significance
Magnesium in Latex varies with
- Clone
- Location
- Fertilising conditions
- Season
Mg++ is an hinderance to MST development and good film formation in the product.
Method
Mg++ being a divalent ion it is estimated by EDTA titration
Reagents
EDTA 0.01M: Dissolve 3.72 g of EDTA in water and make up to 1 litre. A few drops of KOH is added while dissolving
MgSO4 std solution 0.01M: Dissolve 2.46.48 g in 1 litre water
Ammonia-Ammonium Chloride buffer: Dissolve 5.35 g of Ammonium Chloride in 20 ml water add 35 ml 10 M Ammonia and make up to 100 ml.
Eriochrome Black T Indicator: 1 g of EBT in 50 ml EtOH plus 4.5 g of Hydroxyl Amine Hydrochloride
Procedure
Standardisation of EDTA
20 ml standard magnesium solution is pipetted into a china dish (china dish because the white background will show the colour change better) 10 ml of buffer solution is added followed by 2 drops of Erio T indicator. This is titrated against EDTA.
The end point is colour change from Wine Red to Blue
The normality of EDTA is calculated
Estimation of Magnesium
Weigh 5 g of latex into a conical flask and add 10 ml of buffer followed by 2 to 3 drops of Erio T indicator
Titrate against EDTA till the colour changed from Wine Red to Blue
Note the reading
A blank to be done and the value deducted from the above
Interference of Zn ions
This value actually gives the total divalent ions present
If Zinc Oxide is used as a preservative there is likely to be interference
A factor equivalent to the Zinc in ZnO used can be deducted to give Mg present
Zn can be masked using KCN but it being a high poison the use is not recommended
Calculation
% of Mg present (Mg%)= 24.305 x VEDTA X MEDTA X 100
1000 x WLATEX
ppm of Mg = Mg% x1000000 = Mg% x 10000
100
SOME IMPORTANTS POINTS IN TITRIMETRY
Standard Solution:
A known weight of a reagent in a definite volume ia a standard solution
Molar Solution:
When 1 gram molecular weight of a reagent is dissolved in 1 litre it is called a Molar Solution (M)
Normal Solution:
When 1 gram equivalent is dissolved in 1 litre it ia called a Normal Solution (N)
Molar weight & Equivalent Weight
Molar weight is the gram molar weight of a substance & Equivalent weight is the gram molecular weight divided by its valance or combining power
Molar weight of H2SO4 = 2+32+64 = 98
Equivalent wt of H2SO4= 98/2 = 49 (because the valency or combining power is 2)
Standard Solutions
Take an example of standard HCl (1+35.458)
Molecular weight = 36.458
Equivalent weight = 36.458
36.458 g HCl in 1000 mL water = 1.00N solution
When you divide reagent by a number the Normality is also divided by that number
36.458/2 g HCl in 1000 mL water = 1.00/2 N solution
18.229 g HCl in 1000 mL water = 0.50 N solution
When you divide water by a number the Normality is multiplied by that number
18.229 g HCl in 1000/2 mL water = 0.50 x 2 N solution
18.229 g HCl in 500 mL water = 1.00 N solution
CALCULATIONS
Some basic points t be noted in calculations are
1. The chemical you are considering should be confirmed by CAS No. and molecular weight:
MgSO4 has a molecular weight of [24+32+(16x4)]
= (24+32+64)
= 120
- While making a standard solution if you take this weight you will go wrong
- Look for the formula on the container
- You will notice that it is MgSO4.7H2O = 120 + 7(16+2)
= 120+126
= 246
NORMALITY CALCULATIONS
- The basis of Normality calculations is
N1 X V1 = N2 X V2
- There are 4 values and we usually know 3 of them
hence N1 = N2 X V2
V1
Take an example of Mg determination
If N1 (Mg)=0.0056 (Eq wt of Mg = 24.305)
Using the formula N = Eq wt/1000
Mg in 1000 ml will be 0.0056 x 24.305 = 0.136108
Mg in 100 ml (%) will be = 0.136108 x 100 = 0.0136108
1000
Mg ppm will be = 0.0136108 x 1000000 = 136.108
100
Quick Enquiry
To know more about Associated Chemicals feel free to send a message
 Our Sister Concerns
Our Sister Concerns 


Usefull Links
Get In Touch
Assochem Chambers, Bypass, Edapally,
Kochi-682024, Kerala, India.
Phones : +91 9495999349, +91 9388610189, +91 484 2339190, +91 484 2348028
E-mail : nsn@assochem.in, marketing@assochem.in, mail@assochem.in
Support

















